Both passively administered and actively produced antibodies exert. Directly attacks viral pathogens.

Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity Technology Networks
Antibody-mediated regulation of the immune response.

. Antibodies or immunoglobulins Ig are proteins secreted into the extracellular space by B cells to bind to pathogens and antigens. 3 Summary of Cell-Mediated Immunity this takes several days to complete T Cell Memory Like B cells T cells whether T H or CTL also produce extremely long-lived memory cells. Antibodies achieve these effector functions by activating other serum proteins such as complement or by engaging.
Discuss the general effects of stress on immune function. B the response is far faster. One of the advantages of adaptive immunity over innate immunity is.
In other words each antibody recognizes ie. Antibody provides long-term protection against pathogens because it persists for years after the presence of the antigen. Up to 24 cash back Immune response.
There are two types of immunity. Active Immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease. Antibody-mediated immunity definition immunity conferred to an individual through the activity of B cells and their progeny which produce circulating antibodies in response to the presence of a foreign substance and recognize the substance upon renewed exposure.
Most related to antibody-mediated immunity. Since B cells are also Antigen Presenting cells they present antigens to T-cells. Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies.
The active serum components were identified to be immunoglobulins Igs called antibodies. Following are some of the key functions of antibody. This phenomenon is called antibody-mediated feedback regulation and has been known for over 100 years.
It is one of the mechanisms of the active immune system associated with circulating antibodies. D the response targets classes of pathogen instead of specific pathogens. With assistance from helper T cells B cells will differentiate into plasma B cells that can produce antibodies against a specific.
The exact patho-aetiology of SLE remains elusive. 1 the production of antibody by B cells 2 the killing of infected cells by cytotoxic T cells. T cells natural killer cells C B cells.
E a huge variety of cells are produced in response to. Involved in humoral antibody-mediated immunity. As weve learned adaptive immunity involves the following.
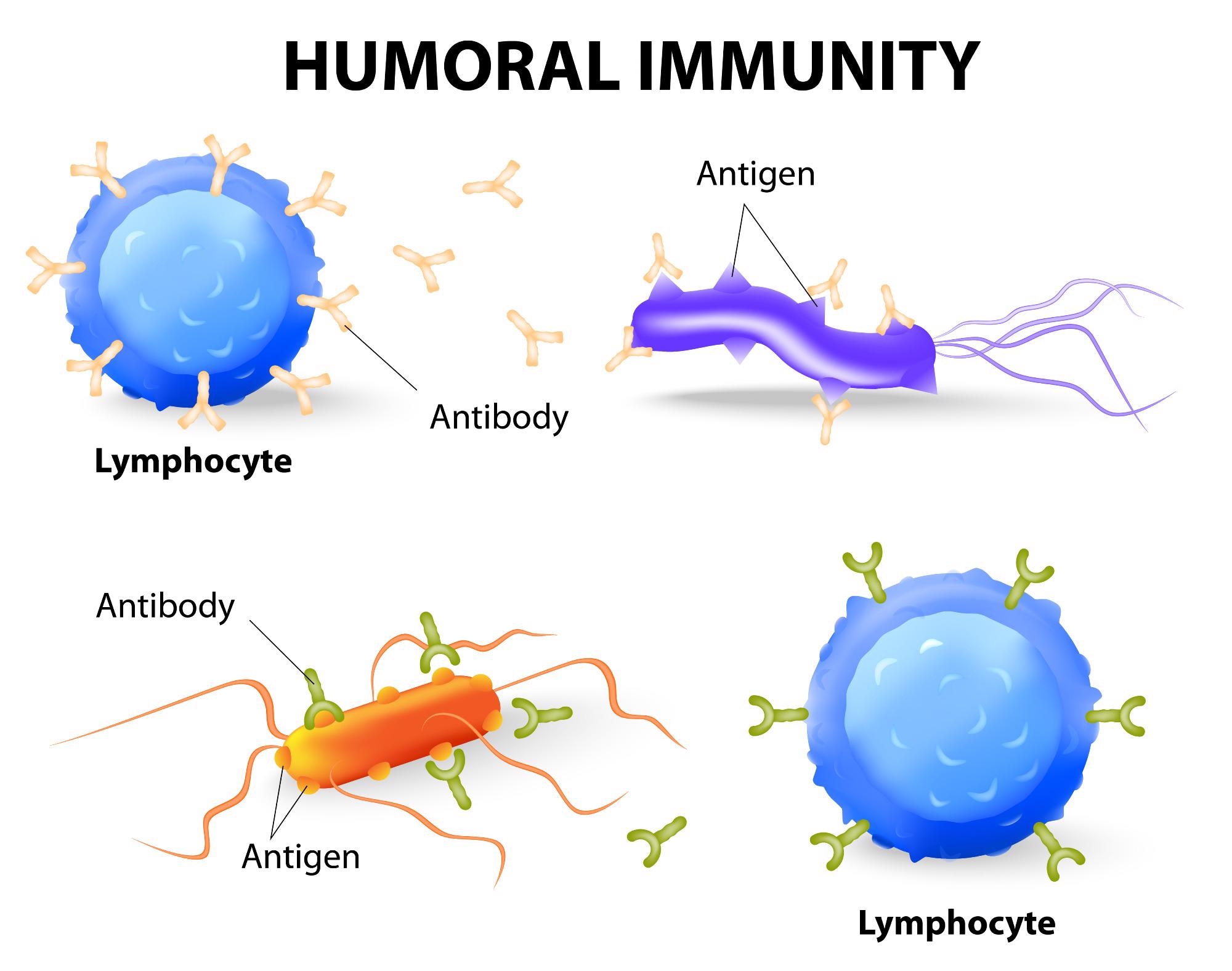
Also referred to as antibody-mediated immunity humoral-mediated immunity involves substances found in the humor or body fluids. What type of immunity is responsible for agglutination of viruses. The enormous diversity of antibodies specific for distinct viruses pathogens and many other antigens is explained by clonal selection whereby specific B-lymphocyte receptors recognize a particular antigen.
Antibody-mediated immunity involves B cells and the production of antibodies in response to a specific antigen. Systemic lupus erythematosus SLE SLE is a prototypic autoimmune disease characterized by multi-organ inflammation with a diverse array of clinical manifestations and production of pathogenic autoantibodies directed against nucleic acids reflecting a global loss of self-tolerance. Activated directly upon subsequent exposure no need for activation signals from other T cells or APCs secondary responses are much more rapid and much more intense than primary responses.
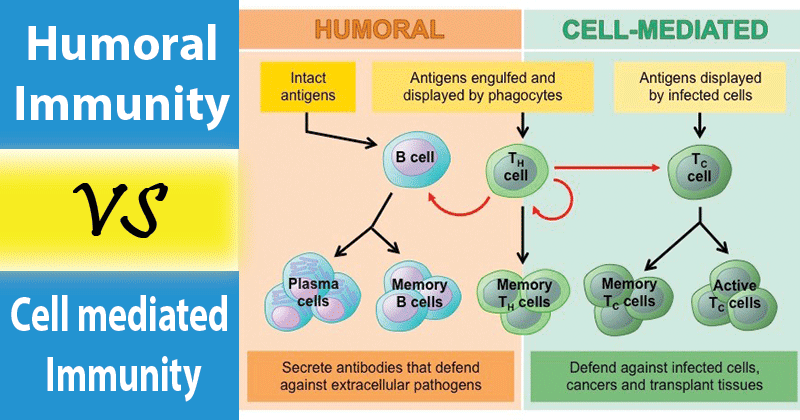
Antibody-mediated humoral and cell-mediated develop concurrently. Immune response is the development of acquired immunity against an antigen Fig. Humoral Cell-Mediated Immunity.
Activation of killer cells. Helper T cells cytotoxic cells memory cells B. Activates the immune system in case of bacterial pathogens.
Which of the following lists contains only cells involved in antibody mediated immunity. Rather cell -mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and the release of various cytokines in response to an antigen. Try this amazing Immune System Chapter 21 quiz which has been attempted 5661 times by avid quiz takers.
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies complement proteins and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluidsHumoral immunity is named so because it involves substances found in the humors or body fluidsIt contrasts with cell-mediated immunityHumoral immunity is also. Cell mediated immunity 18. The steps involved in the process are.
Explain the origin of autoimmune disorders immunodeficiency diseases and allergies and give examples of each. A the response is targeted against a single pathogen. Involved in cell-mediated immunity.
This range of antibody activities provides a response to rapid antigen-specific B cells production during infections. B colls dendritic cells macrophages E Neutrophils macrophages phagocytes 71. Which of the following best describes the immunity gained from a vaccine.
The two arms of the immune response. B cell activation by helper T cells Antibody production by plasma cells Destructionelimination of target antigen-antibody complex. Activation of the complement system.
Antibodies are the chief secretory product of B cells. Antibodies administered in vivo together with the antigen they are specific for can regulate the immune response to that antigen. Also explore over 36 similar quizzes in this category.
A Antibody-mediated immunity is called humoral immunity because it is mediated by antibodies macromolecules in the extracellular fluid complement proteins present in the blood. In doing so they can prevent infection neutralize toxins and stimulate the immune response. Contacts a given antibody is called the epitope aka antigenic determinant.
Explain primary and secondary responses to antigen exposure and the role of antibodies. Antibody-Mediated Humoral Immunity Involves production of antibodies against foreign antigens. They help to activate B cells and aid in antibody production against antigens which are T-dependent.
Answers 1 P Priyanka Kumari. Transfer of antibodies from mother to offspring. Peyors patches are found in the distal.
- Antibodies are produced by a subset of lymphocytes called B cells. Humoral immunity is also called antibody-mediated immunity. C the ability to recognize antigens common to many microbes.
B In vaccination a preparation of antigenic proteins of pathogen or inactivatedweakened pathogen vaccine is introduced into the body. The protective activities of antibodies against infection or reinfection by common organisms eg streptococci and staphylococci. Briefly summarize the bodys response to a foreign antigen.
Plasma cells memory cells D. Immune response occurs due to activation of B andor T cells on recognition of specific antigen. Active immunity can be acquired through natural immunity or vaccine-induced immunity.
Protective attachment to antigens. Antibody-Mediated Humoral Immunity. This type of immunity is also called.
B lymphocytes with receptors to a specific antigen react when they encounter that antigen by producing plasma cells which produce antigen-specific antibodies and memory cells which enable the body to produce.

Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity Technology Networks
Humoral Vs Cell Mediated Immunity
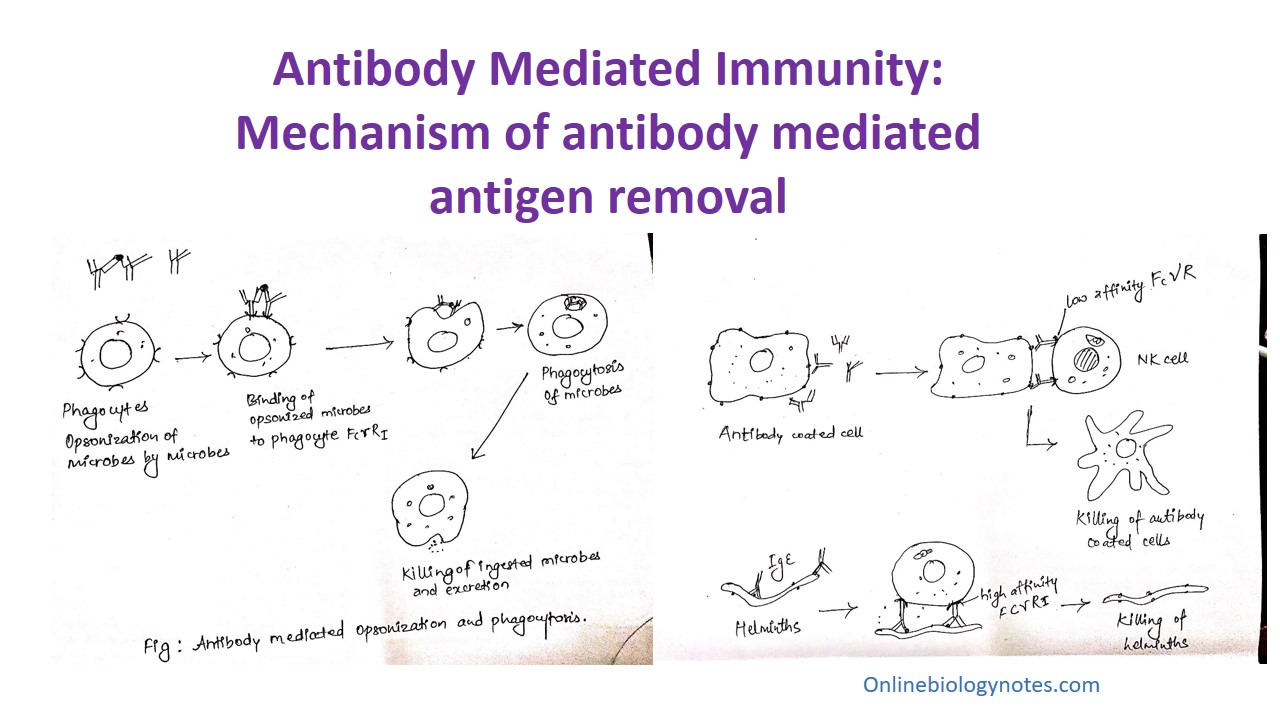
Antibody Mediated Immunity Ami Activation And Mechanism Of Antibody Mediated Antigen Removal Online Biology Notes
0 Comments